Beijing and Singapore launch Interoperable Digital Documents Against Payment Trade Cooperation
Beijing Two-Zone Office and Singapore’s Infocomm Media Development Authority Launch World’s First Interoperable Digital Documents against Payment Cooperation, Empowering Global Trade and Financial Services with End-to-End Digitalisation
Jointly driven by the Office of the Leading Group for the Work of the China (Beijing) Pilot Free Trade Zone and the Integrated National Demonstration Zone for Opening Up the Services Sector (referred to as the “Beijing Two-Zone Office”) and Singapore’s Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA), the world’s first project on interoperable digital Documents against Payment (D/P) for paperless live trades was concluded successfully on 9 April 2025. This milestone follows the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on International Information Industry and Digital Trade Harbour Cooperation by the Beijing Municipal Commerce Bureau (Beijing Two-Zone Office) and IMDA in December 2023. Guided by the Beijing Two-Zone Office and executed by the Beijing Borui Opening-Up Policy Research Institute, this project marks another achievement in Beijing-Singapore digital economy collaboration, introducing a novel interoperable trade finance model for international trade and financial services, paving the way for business-as-usual digital operations.
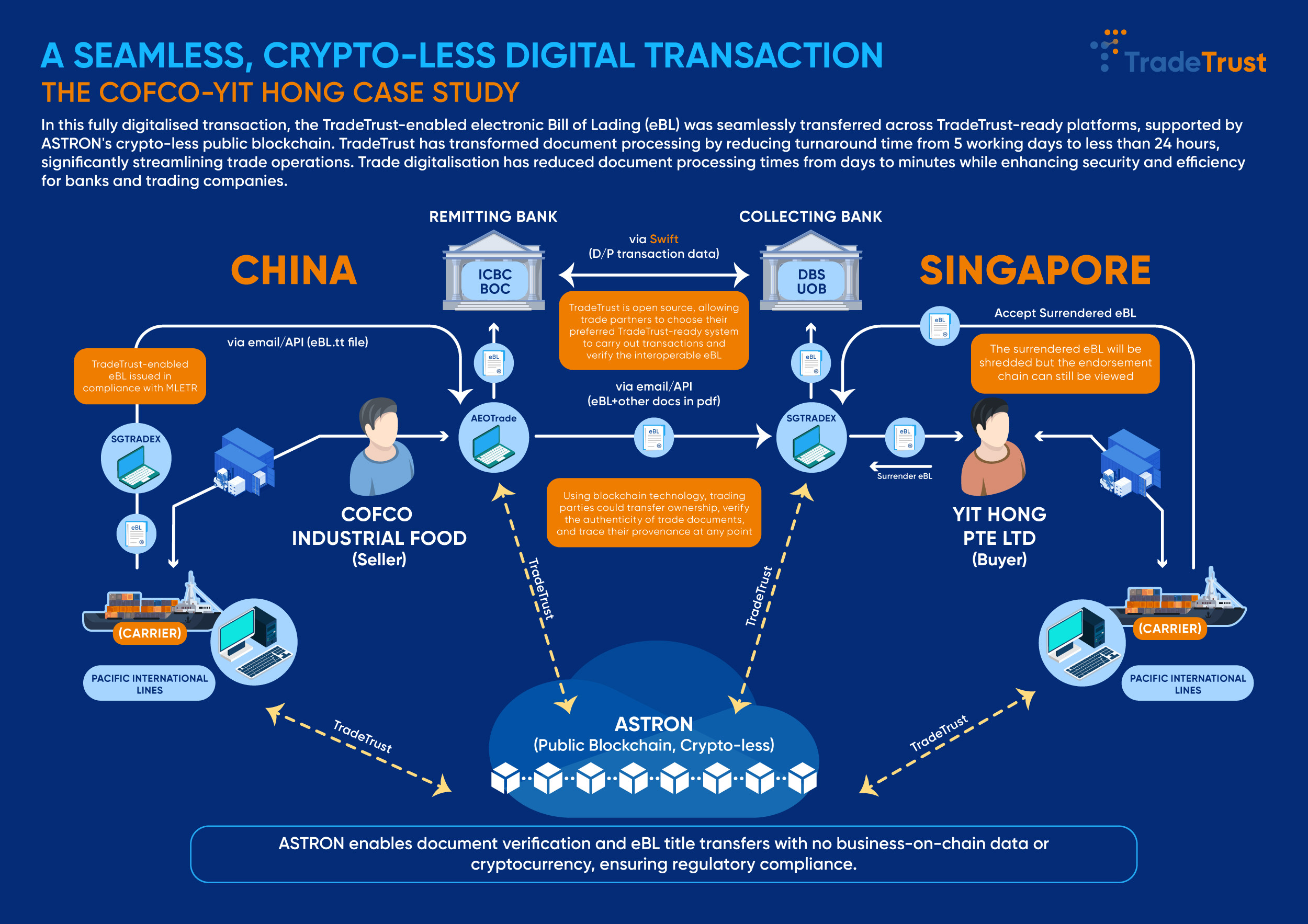
It was jointly executed by COFCO Industrial Food (also known as China Processed Food) and Yit Hong Pte Ltd in Singapore, utilising the B2B cross-border e-commerce model (China Customs Code: 9710) to export canned food containers via sea freight from Xiamen Port to Singapore Port, with shipping managed by carrier - Pacific International Lines (PIL). Key participants included the Bank of China (BOC) and Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) as remitting banks, and Singapore’s DBS and United Overseas Bank (UOB) as collecting banks, to support D/P transaction using electronic Bill of Lading (eBL).
The project achieved cross-platforms interoperability between different digital trade infrastructures (AEOTrade and SGTraDex), enabling secure and efficient eBL and other trade documents exchange that offer authentication, traceability of origin, and ownership transfers among carriers, cargo owners, banks, and other stakeholders. The eBL, serving as a digital document of title, not only streamlined customs clearance and logistics, but also addressed risks such as loss or tampering inherent in traditional paper-based documentary collections, and enhancing trade security and credibility. It also transformed the end-to-end international trade processes, covering contract signing, document circulation, and payment settlement, and facilitated the fully online electronic document flows between collecting and remitting banks, significantly shortening transaction cycles, reducing time costs, and boosting trade efficiency.
According to Chinese participating banks, BOC and ICBC, the transaction demonstrated that replacing traditional cross-border paper document mailing with digital transmission had reduced document circulation costs by 30%, and effectively mitigated risks like document fraud or loss. In addition, COFCO Industrial Food pointed out that with the traditional paper-based D/P processes, the period from shipment to payment settlement typically took around 20 days, while digitisation slashed this to just five days, minimising delays in document processing and transfer while significantly improving capital turnover efficiency. Participating enterprises in Singapore also confirmed similar results of reducing costs and improving efficiency. Yit Hong has reduced documentation handling time by 60%, enabling faster goods claims without courier delays. Based on PIL’s experience, the processing time of Bills of Lading (BL) has been dramatically reduced from 5-10 days of couriering paper BL to just 8 minutes per transaction digitally, while eliminating the risk of documents being lost in transit. Separately, DBS highlighted that this transaction reinforced the importance of interoperability and common standards in accelerating trade digitalisation and promoting a more efficient global trade ecosystem, while also addressing the scalability challenges of closed-loop platforms. UOB also recognised from this project that the digital issuance, transfer and endorsement of a TradeTrust-enabled eBL allowed banks to efficiently establish the authenticity of a BL without a separate validation process. When scaled, this can help to mitigate risk of trade finance fraud and strengthen confidence in cross-border trade finance.
Prior to this, COFCO and Yit Hong had implemented end-to-end interoperable digital trade collaborations in October 2023 (with PIL as the carrier) and May 2024 (with Maersk as the carrier), utilising telegraphic transfer (T/T) payments. These successful pilots laid a solid foundation for the current digital D/P implementation, expanding interoperable trade financing process in international trade finance.
Moving forward, the Beijing Two-Zone Office and IMDA will leverage the “AEOTradeChain+TradeTrust” framework to explore broader end-to-end interoperable digital trade scenarios. These efforts will engage more countries, regions, industries, and business types, inviting participation from cargo owners, financial institutions, logistics providers, and other stakeholders to jointly advance the digital transformation of global trade and financial services, injecting new momentum into the sector.
Collaboration bridges digital trade platforms: AEOTrade and SGTraDex sign MoU
As Singapore’s digital infrastructure for supply chain data, SGTraDex enables trusted and structured cross-border data exchange, enhancing traceability, transparency, and confidence in trade. This successful collaboration demonstrated the transformative potential of interoperable digital ecosystems, culminating in the signing of a MoU with AEOTrade. As part of the MoU, both parties will explore opportunities to integrate their infrastructure and solutions to support digital documents, such as eBLs, to enhance connectivity between the China and Singapore’s trade ecosystems. These include aligning strategic plans, conducting joint feasibility studies, and ensuring compliance with applicable regulations.
Learn from participants' insights in this video
Transactional Flowchart of Processes
This press release was published by Beijing Two-Zone Office.

